Mineral properties and mineral structure
Mineral properties and mineral structure
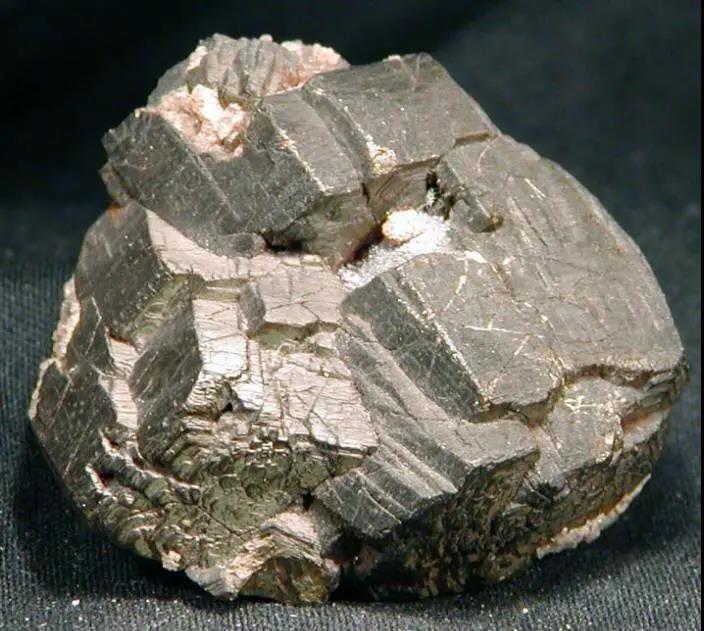
Titanium-bearing minerals mainly include ilmenite, rutile, anatase, brookite, perovskite, sphene, titanomagnetite, etc., among which ilmenite and rutile are the main titanium smelting minerals.
The molecular formula of ilmenite is FeTiO3, theoretically containing 52.66% of TiO2 and 47.34% of FeO. It is a steel gray to black ore, with a Mohs hardness of 5-6, a density of 4.72g/cm3, medium magnetism, good conductor, and normal type. The qualitative identity is mixed with magnesium and manganese, or contains fine scaly hematite inclusions.
The molecular formula of rutile is TiO2, containing 60% Ti and 40% O. It is a brownish-red mineral, often containing a mixture of iron, niobium, chromium, tantalum, tin, etc., with a Mohs hardness of 6, and a density of 4.2~4.3g/cm3. Magnetism, good conductivity, dark brown when iron content is high, rutile is mainly produced in placers.
Application fields and technical indicators
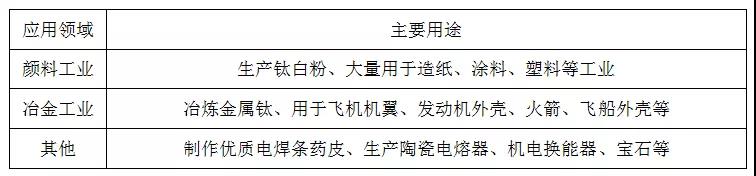
Rutile and ilmenite are the main raw materials for smelting metallic titanium, manufacturing titanium dioxide, welding rods, and welding fluxes.
Table 1. Main uses of rutile and ilmenite
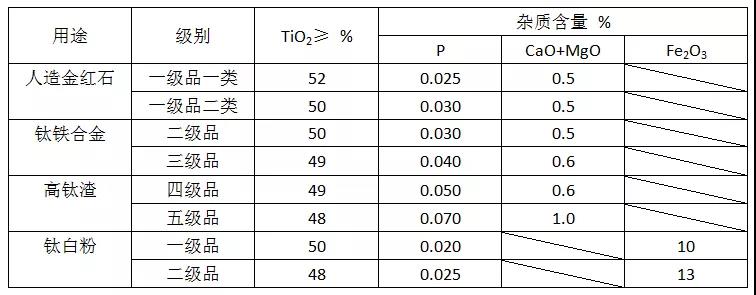
Table 2. Titanium Concentrate Quality Standard
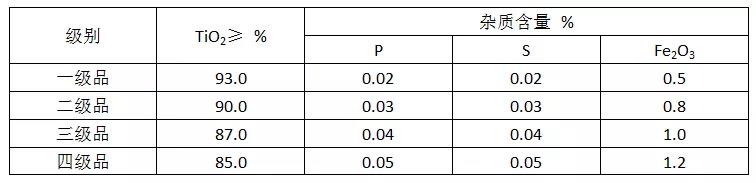
Table 3. Quality Standards of Natural Rutile
Processing technology
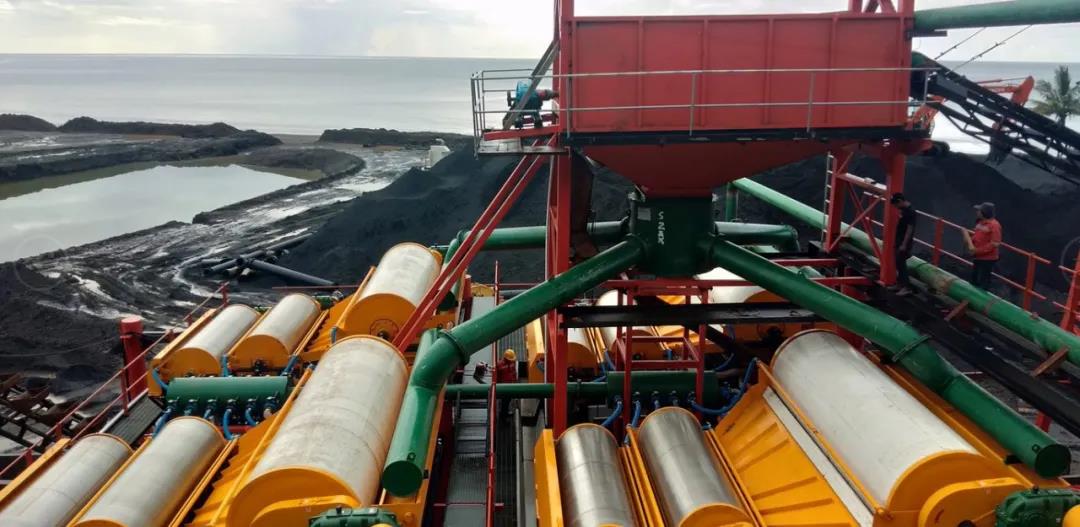
Usually ilmenite and rutile ore are accompanied by a variety of other minerals, such as magnetite, hematite, quartz, feldspar, amphibole, olivine, garnet, chromite, apatite, mica, pyroxene Stones, etc., are generally selected by gravity separation, magnetic separation, electric separation and flotation.
Gravity beneficiation
This method is generally used for rough separation of titanium-containing placer or crushed titanium-containing primary ore. The density of titanium-containing minerals is generally greater than 4g/cm3. Therefore, most gangues with a density of less than 3g/cm3 can be removed by gravity separation. Mineral removal. Gravity separation equipment includes jig, spiral concentrator, shaker, chute, etc.
Magnetic separation
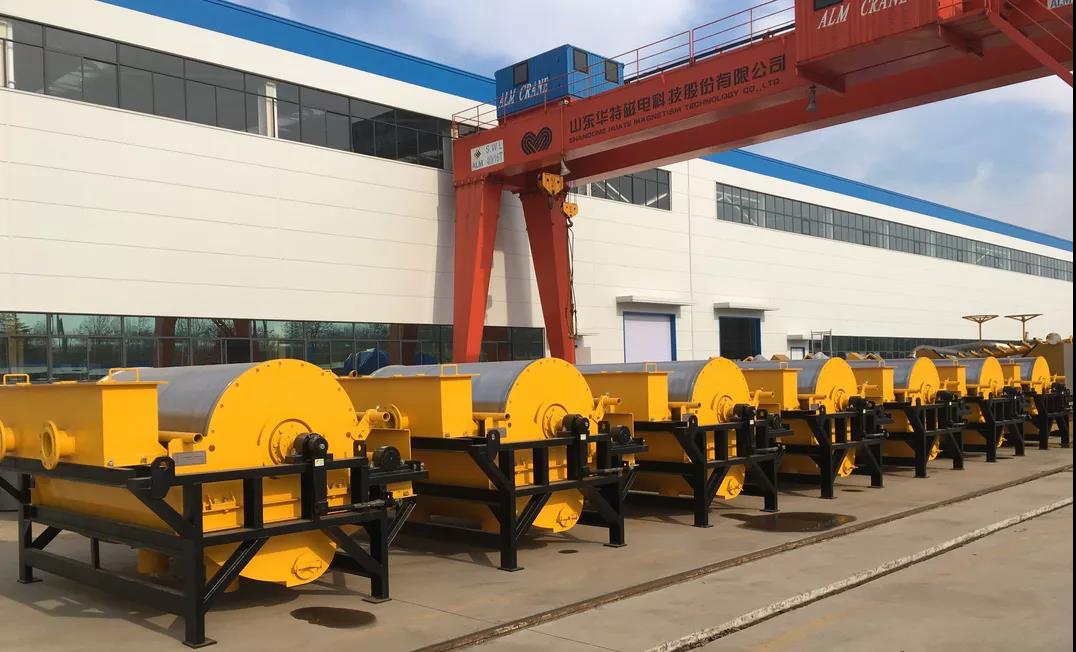
The magnetic separation method is widely used in the selection of titanium-containing minerals. We can use weak magnetic separation to separate magnetite, and then use strong magnetic separation to separate medium-magnetic ilmenite. For example, the concentrate contains more iron oxide or For iron silicate, the gravity separation method should be used to remove impurities with a small specific gravity. In industry, both dry and wet magnetic separation are used.Magnetic separation equipment mainly includes cylindrical magnetic separator, plate magnetic separator, vertical ring high gradient magnetic separator, etc.
Drum magnetic separator
High-intensity magnetic plate magnetic separator
Electrostatic beneficiation
It mainly uses the difference in conductivity between different minerals in the titanium-containing coarse concentrate for selection, such as the separation of rutile, zircon, and monazite. The electric separators used are roller type, plate type, sieve plate type and so on.
Flotation
It is mainly used to separate fine-grained titanium-containing ore. Commonly used flotation reagents include sulfuric acid, tall oil, oleic acid, diesel oil and emulsifiers. The beneficiation methods include positive flotation of titanium and reverse flotation of gangue minerals.
Joint beneficiation
For placerite with more associated minerals, the difference in specific magnetic susceptibility, density, conductivity, and floatability between minerals can be used to separate the minerals by the combined process of “magnetic, heavy, electric, and float”.For example, the coastal alluvial sand contains minerals such as magnetite, ilmenite, rutile, zircon sand, monazite, sea sand, etc.First, the magnetite is separated by weak magnetic field, and then the ilmenite is separated by the vertical ring with medium field strength. The high field strength vertical ring of the vertical ring tailings removes other iron-bearing minerals, and then the smaller specific gravity is separated by the gravity separation method. For sea sand, the heavy minerals are rutile and zircon sand. The rutile with better conductivity can be selected by electric separation, so as to complete the effective separation of this kind of mineral.
Vertical ring high gradient magnetic separator
Beneficiation case
There are magnetite, titanomagnetite, ilmenite, rutile, zircon sand, sea sand and a small amount of iron-bearing minerals in alluvial placers in Indonesia,Among them, ilmenite, rutile, and zircon sand are the main target minerals, and titanomagnetite, iron oxide, iron silicate, and sea sand are impurities. The minerals are separated and qualified by physical methods such as magnetic separation and gravity separation. All concentrate products.Among them ilmenite, rutile, zircon are the main target minerals, ilmenite, iron oxide, iron silicate, sea sand as impurities,Through magnetic separation, gravity separation and other physical methods, the minerals are separated and qualified concentrate products are selected.
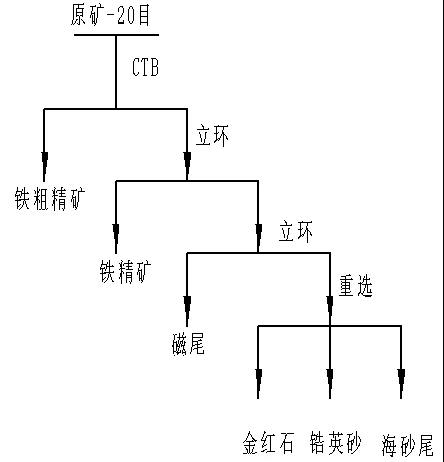
The particle size of alluvial sand is uniform, and the general particle size is 0.03 ~ 0.85 mm. The qualified concentrate products such as ilmenite, rutile and zircon sand are separated by the combined beneficiation process of weak magnetic separation + medium magnetic separation + high magnetic separation + gravity separation.
Fig 1. Combined beneficiation test process of alluvial sand ore
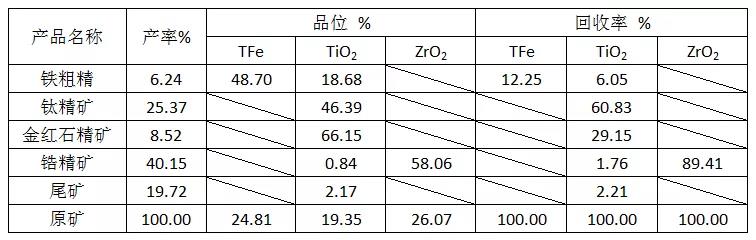
Table 4. Indexes of Joint Beneficiation Test
Using the difference in specific magnetic susceptibility and density between minerals, through the combined process of weak magnetic + strong magnetic + gravity separation, ilmenite concentrates with a yield of 25.37%, a TiO2 grade of 46.39%, and a recovery rate of 60.83% were selected.rutile concentrate with yield of 8.52 %, TiO2 grade of 66.15 % and recovery of 29.15 % ;Zircon placer concentrate with a yield of 40.15%, a ZrO2 grade of 58.06%, and a recovery rate of 89.41%.Iron concentrate contains more titanomagnetite, so qualified iron concentrate products cannot be selected.
Post time: Mar-20-2021