[Huate Mineral Processing Encyclopedia] Revealing the secrets of Kaolin: a gorgeous transformation from soil to high-tech materials
Kaolin is a non-metallic mineral, a kind of clay and clay rock mainly composed of Kaolinite clay minerals. Because it is white and delicate, it is also called Dolomitic soil. It is named after Gaoling Village, Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province. Its pure Kaolin is white, delicate, soft and earthy, and has good physical and chemical properties such as plasticity and fire resistance. Its mineral composition is mainly composed of Kaolinite, Halloysite, Hydromica, Illite, Montmorillonite, Quartz, Feldspar and other minerals.
Kaolin is a common and very important clay mineral in nature. It is formed by the weathering of feldspar or other silicate minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks in acidic media lacking alkali metals and alkaline earth metals.
01 Classification
Soil classification
The minerals contained in Kaolin in nature are mainly divided into clay minerals and non-clay minerals. Among them, clay minerals mainly include Kaolinite minerals and a small amount of Montmorillonite, mica and Chlorite; non-clay minerals mainly include feldspar, quartz and hydrated minerals, as well as some iron minerals such as hematite and Rhosite, Iron ore, Limonite, etc., titanium minerals such as Rutile, etc. and organic matter such as plant fiber, etc. It is mainly clay minerals that determine the properties of Kaolin.
Cause classification
Based on the origin of Kaolin deposits and based on the differences in Mineralization geology, geographical conditions, deposit scale, ore body morphology and occurrence characteristics, ore material components reflected in different Mineralization processes, the "Kaolin Mine Geological Exploration Code" will China's Kaolin deposits are divided into three types and six subtypes.
Weathering type: It is further divided into weathering residual subtype and weathering leaching subtype.
Hydrothermal alteration type: It is further divided into hydrothermal alteration subtype and modern hot spring alteration subtype.
Sedimentary type: It is divided into sedimentary and sedimentary-weathering subtypes and Kaolinite claystone subtype in coal-bearing strata.
Industrial Type
Based on the genesis of Kaolin deposits, the "Kaolin Mine Geological Exploration Specifications" divides China's Kaolin deposits into three types and six subtypes according to the differences in Mineralization geology, geographical conditions, deposit scale, ore body morphology and occurrence characteristics, and ore material components reflected by different Mineralization processes. According to their texture, plasticity, and the mass fraction of sand, they are divided into three types:
Hard Kaolin: hard and non-plastic, becomes plastic after being crushed and ground.
Soft Kaolin: soft, highly plastic, sandy mass fraction <50%.
Sandy Kaolin: soft texture, weak plasticity, sand mass fraction> 50%.
02 Origin
China's Kaolin mineral resources rank among the top in the world, with 267 proven mineral deposits and proven reserves of 2.91 billion tons. Among them: my country's non-coal construction Kaolin resources rank fifth in the world. The proven reserves are 1.468 billion tons, mainly concentrated in Guangdong, Shaanxi, Fujian, Jiangxi, Hunan and Jiangsu provinces, accounting for 84.55% of the country's total reserves; China's coal-bearing construction Kaolin (Kaolinite) reserves rank first in the world, with proven reserves of 1.442 billion tons, mainly distributed in Datong, Huairen, Shuozhou, Shanxi, Jungar, Wuda, Inner Mongolia, Huaibei, Anhui, Hancheng, Shaanxi, etc., among which the Jungar coalfield in Inner Mongolia has the most resources.
There are five major Kaolin deposits in China:
(1) Jiepai Town, Hengyang County, Hunan Province is rich in mineral resources. The reserves of Kaolin, Nepheline, Feldspar and Quartz reach 200 million tons, and there are nearly 40 mining and mineral processing companies. The Dapailing mining area (mainly Kaolin mines) has a single mine reserve of 80 million tons, which ranks first in Asia. The town's annual mining output is more than 500,000 tons, supplying hundreds of ceramic factories across the country.
(2) Kaolin in the Maoming area. The Kaolin mineral in the Maoming Basin is a sedimentary rock weathered eluvial sub-type deposit. Its quartz and other sand content is greater than 50%, so it is called sandy Kaolin mineral. In terms of origin, Maoming Kaolin has gone through three stages of weathering residue - transportation and self-grinding - and then weathering. The Kaolin is completely weathered, and the wafers are mainly monolithic with fine particle size. Mainly used as raw materials for papermaking coatings.
(3) Longyan Kaolin is a weathered residual Kaolin deposit. Since the iron content is less than 0.3%, titanium is less than 0.02%, and it contains a certain amount of low-temperature solvent element (Li2O), it is an ideal raw material for electric porcelain, high-end daily use, and artistic porcelain.
(4) Suzhou Yangshan Kaolin, this deposit is hydrothermal alteration Kaolin. The chemical composition of Suzhou Yangshan mud with pure texture is very close to the theoretical composition of Kaolinite. The Al2O3 content can be as high as about 39.0%, with white color and fine particles. Mainly used for catalyst carriers and chemical raw materials.
(5) Hepu Kaolin. It is a weathered residual Kaolin deposit. Mainly used as raw materials for building ceramics.
(6) Northern coal series Kaolin. It is a sedimentary Kaolinite, mainly distributed in my country's coal-producing areas, and can be used in construction, coatings, paints and papermaking coatings - coal-based soil.
The above-mentioned six major production areas account for more than 80% of China's output, and are also major representatives in terms of resource types.
03 Use
Kaolin has a wide range of uses, mainly due to its plasticity, adhesion, certain dry strength, sintering properties and post-fired whiteness, making it the main raw material for ceramic production; it is white, soft, highly dispersible, adsorbable Its excellent process properties such as chemical properties and chemical randomness make it widely used in the paper industry. In addition, Kaolin is also widely used in industrial sectors such as rubber, plastics, refractories, and petroleum refining, as well as in cutting-edge technologies in agriculture and national defense. Mainly used in ceramic industry, coatings, refractory materials, papermaking, paint, rubber, high-grade porcelain, wires and cables, industrial plastics, chemical industry fillers, inks, food, cosmetics, medicines, etc., replacing lithopone and part of titanium in paints and coatings White powder and other expensive materials.
04 Processing Technology
In order to separate non-clay minerals and organic matter such as quartz, feldspar, mica, iron minerals, titanium minerals, etc. in Kaolin and produce Kaolin products that can meet the needs of various industrial fields, in addition to using gravity separation, flotation, magnetic separation, etc. to purify and remove impurities from Kaolin, sometimes it is also necessary to use deep processing methods such as chemical bleaching, ultrafine flaking, calcination, and surface modification to treat Kaolin.
(1) Hydraulic classification
Hydraulic classification includes spiral classification (separation of +1mm coarse sand), sedimentation tank classification (separation of +0.053mm fine sand), hydrocyclone classification (separation of -0.053mm fine sand), centrifugal classifier or small diameter hydrocyclone classification (for ultrafine particle classification of 0.002-0.010mm).
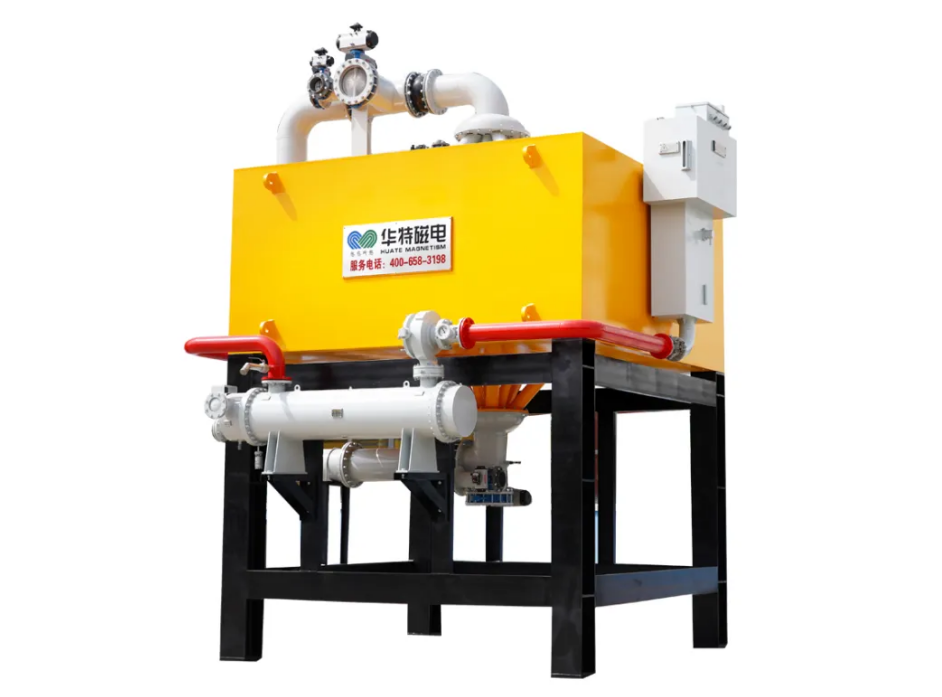
(2) High gradient magnetic separation
Magnetic field strength of more than 1 600 kA/m is generated by using magnetic concentrator media to remove Fe2O3 and TiO2 from Kaolin and produce paper coatings and high-grade ceramic raw materials.
(3) Selective flocculation
By adding flocculants, impurities such as fine-grained quartz, pyrite, alunite, etc. are selectively separated to produce blade-coated Kaolin. Commonly used flocculants include sodium hexametaphosphate, ammonium polyacrylamide, water glass, etc.
(4) Chemical bleaching
Bleaching agents such as insurance powder are added to reduce the high-valent iron in limonite and hematite in Kaolin to soluble ferrous iron, or oxidants are added to oxidize pyrite and dyeing impurities to improve the whiteness of Kaolin.
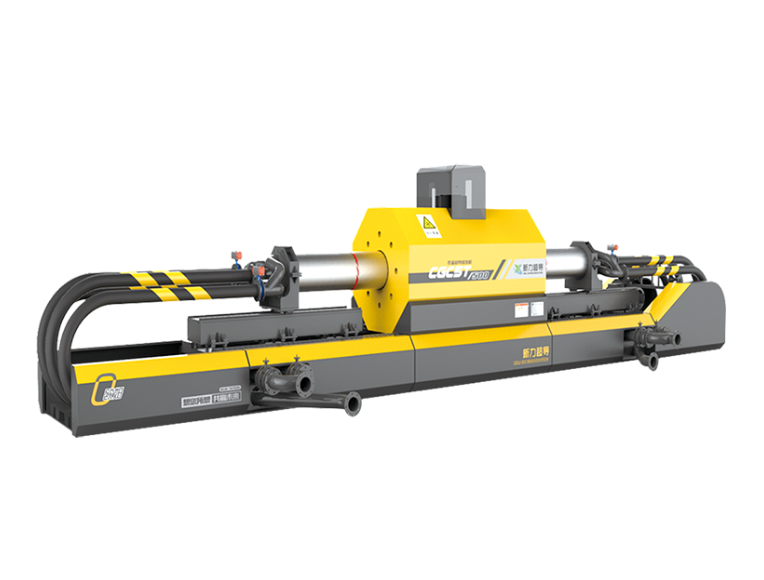
(5) Peeling
In the flaking machine, stirring fine medium balls are used to produce a grinding effect, so that the Kaolin aggregate particles are separated into thin crystals, producing blade-coated Kaolin with a particle size of less than 2μm and a content of more than 90%.
(6) Calcination
When calcined at 800-1000℃, Kaolin loses water, phase transformation occurs, and some impurities volatilize, which improves the whiteness and insulation of Kaolin and is used to produce cables and rubber and plastic fillers. Calcination is a necessary processing method for coal-based (hard) Kaolin.
(7) Surface modification
The Kaolin clay is coated with a coupling agent, etc., to increase the amount of Kaolin clay added in plastic rubber, and is used to treat Kaolin clay fillers for rubber plastics.
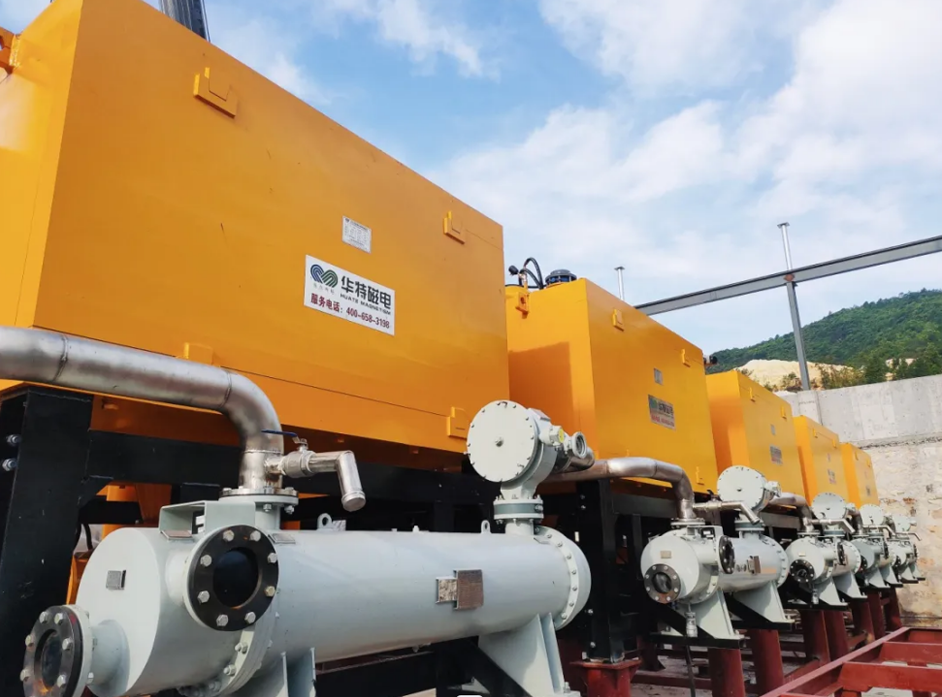
Among them, magnetic separation is a physical mineral separation method widely used in the field of mineral processing. Its basic principle is to use the magnetic differences of the minerals themselves to achieve separation. According to the magnetized properties of minerals, magnetic separation can be divided into strong magnetic separation, weak magnetic separation, reverse magnetic separation and high gradient magnetic separation to meet the needs of different minerals. Mineral processing equipment mainly includes plate magnetic separators, vertical ring high gradient magnetic separators, electromagnetic slurry high gradient magnetic separators, low temperature superconducting magnetic separators, etc.
05 Mineral processing application cases
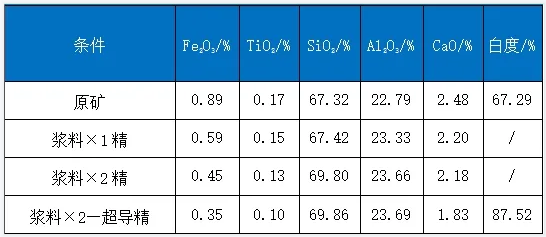
Process 1: Taking a foreign Kaolin clay as an example, the main impurities in this sample include iron oxide, titanium oxide, and iron silicate. In the raw ore, the impurity contents of Fe2O3 and TiO2 are 0.89% and 0.17% respectively, while the whiteness reaches 67.29%.
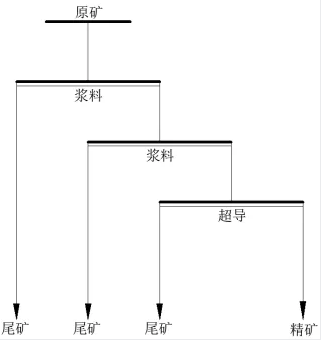
In order to effectively remove these impurities, we determined the following test plan: First, pass the raw ore through an electromagnetic slurry magnetic separator for two magnetic separation processes, rough separation and fine selection, to initially remove most of the impurities. Then, the obtained concentrate is further purified through a superconducting magnetic separator to further reduce the impurity content and improve the quality of Kaolin.
Test flow chart
It can be seen from the test results that the raw ore can be separated by electromagnetic slurry + electromagnetic slurry + superconducting magnetic separation to obtain a Kaolin concentrate product with Fe2O3 0.35% and whiteness 87.52%.
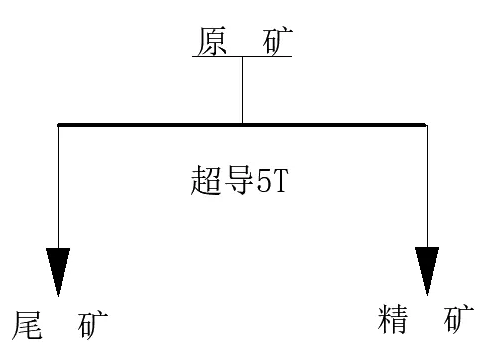
Process 2: Raw ore undergoes superconducting 5T magnetic separation. The test process is shown in Figure 2, and the test results are shown in Table 2.
FIG. 2 Experimental flow of beneficiation
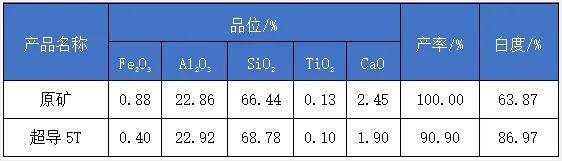
The raw ore was subjected to superconducting 5T magnetic separation to obtain a Kaolin concentrate product with Fe2O3 0.40%, Al2O3 22.92%, SiO2 68.78%, TiO2 0.10%, CaO 1.90%, whiteness 86.97%, and a yield of 90.90%.
As a multifunctional industrial raw material, Kaolin has broad application prospects. With the continuous advancement of science and technology and the sustainable development of the industry, Kaolin will play an important role in more fields. In the future, we look forward to further expanding the application scope of Kaolin through more in-depth research and technological innovation, achieving more efficient and sustainable utilization, and making greater contributions to the development of human society. At the same time, we should also pay attention to the environmental problems that may arise during the mining and processing of Kaolin, and take active measures to ensure that the rational development of Kaolin resources is coordinated with the protection of the ecological environment.
Post time: May-13-2024