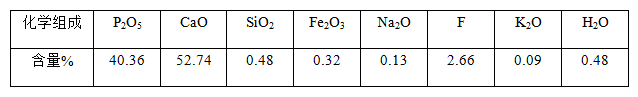Phosphate rock refers to the general term for phosphate minerals that can be used economically, mainly apatite and phosphate rock. Yellow phosphorus, phosphoric acid, phosphide and other phosphates are used in medical, food, matches, dyes, sugar, ceramics, national defense and other industrial fields.
Ore Properties and Mineral Structure
There are about 120 kinds of phosphorus-containing minerals known in nature, but as phosphorus-containing industrial minerals are mainly phosphate minerals in apatite and phosphate rock. Apatite [Ca5(PO4)3(OH,F)] is a mineral whose main component is calcium phosphate. It has different names due to the different elements it contains, such as fluorine and chlorine. Common phosphorus-containing minerals are: Fluorapatite, chloroapatite, hydroxyapatite, carbonapatite, fluorocarbon apatite, carbon hydroxyapatite, etc. The theoretical content of P2O5 is between 40.91 and 42.41%. The additional anions F, OH, CO3, and O in phosphate rock can replace each other, and there are many isomorphic components, so the chemical composition of the mineral changes greatly.
Typical chemical composition of apatite
- Chemical components 2.ContentApplication areas and index requirementsPhosphate rock is mainly used as the raw material of phosphoric acid fertilizer and various phosphorus compounds, and is widely used in the fields of chemical industry, medicine, pesticide, light industry and military industry.Processing TechnologyBeneficiation and purification
Phosphate rock can be divided into siliceous type, calcareous type, and silicon (calcium)-calcium (silicon) type. The associated minerals are mainly quartz, flint, opal, calcite, feldspar, mica, limestone, dolomite, rare earth. , magnetite, ilmenite, limonite, etc., flotation method is the most important beneficiation method for apatite.
The principle technological process mainly includes: flotation + magnetic separation combined process, grinding + classification + flotation process, stage grinding + stage separation process, roasting + digestion + classification process.
Oil-water composite cooling vertical ring high gradient magnetic separator
Processing of Phosphate Compounds of Phosphate Fertilizers
Phosphate fertilizer manufacturing is to convert phosphate minerals into phosphates that are easily absorbed by plants through the process of beneficiation, high temperature, and synthesis. Ammonium phosphate is a high-efficiency compound fertilizer made from phosphoric acid in ammonia water. Yellow phosphorus is obtained by heating phosphate rock mixed with quartz sand and coke at 1500°C in an electric furnace. There are two production methods of phosphoric acid: sulfuric acid extraction method and peroxy combustion absorption method.
Beneficiation example
The fineness of iron tailings in Hebei is -200 mesh, accounting for 63.29%, the total iron TFe content is 6.95%, and the P2O5 content is 6.89%. Iron is mainly iron oxide such as limonite, iron silicate and magnetite in the form of continuous inclusions; phosphorus-containing minerals are mainly apatite, gangue minerals are quartz, feldspar, calcite, etc. It is more closely combined with phosphorus minerals. The purpose of the test is to select various iron-bearing minerals by magnetic separation, and apatite is enriched in the magnetic separation tailings.
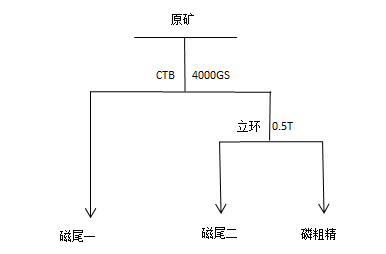
According to the properties of the samples, the process of beneficiation is determined as follows: the selected raw ore – 200 mesh with a fineness of 63.29%, is made into a slurry with a concentration of 30%, and the continuous magnetic iron is selected by the CTB4000GS weak magnetic field, and the tailings are selected by the vertical ring 0.5T weak Magnetic iron oxide and iron silicate minerals.
Process flow of magnetic separation iron removal test of phosphorus-containing iron tailings
The iron-containing phosphorus iron tailings have undergone the iron removal process of one roughing and one sweeping twice, and the qualified iron concentrate products could not be selected from the magnetic material. The phosphorus content in the phosphorus coarse concentrate was increased from 6.89% to 10.12%, and the phosphorus recovery rate was 79.54%. %, the iron removal rate was 75.83%. In the comparison test of different field strengths of Lihuan 0.4T, 0.6T and 0.8T, it was found that the low field strength of Lihuan 0.4T resulted in too much iron in the phosphorus coarse and refined, and the high field strength of 0.8T caused the loss of phosphorus in magnetic materials. Big. The selection of suitable magnetic separation conditions is beneficial to improve the beneficiation index of the flotation operation of the lower phosphate rock.
Scope of mineral processing technology services
Scope of technical services of Huate Mineral Processing Engineering Design Institute
①Analysis of common elements and detection of metal materials.
②Preparation and purification of non-metallic minerals such as English, long stone, fluorite, fluorite, kaolinite, bauxite, leaf wax, baryrite, etc.
③The beneficiation of black metals such as iron, titanium, manganese, chromium and vanadium.
④ Mineral beneficiation of weak magnetic minerals such as black tungsten ore, tantalum niobium ore, pomegranate, electric gas, and black cloud.
⑤ Comprehensive utilization of secondary resources such as various tailings and smelting slag.
⑥ There are ore-magnetic, heavy and flotation combined beneficiation of ferrous metals.
⑦Intelligent sensing sorting of metallic and non-metallic minerals.
⑧ Semi-industrialized continuous selection test.
⑨ Ultrafine powder processing such as material crushing, ball milling and classification.
⑩ EPC turnkey projects such as crushing, pre-selection, grinding, magnetic (heavy, flotation) separation, dry raft, etc.
Post time: Mar-30-2022